Chroma, a powerful and versatile database management system, has become a cornerstone in the world of data storage and retrieval. In this article, we will demonstrate how to connect Chroma and how to use it in UBOS.
Connect (initial) to the Chroma Client
In the "function" node, you need to install two npm libraries: chromadb and openai.
To initialize the Chrome client, you need to input the following code:
const { ChromaClient } = chromadb;
const { OpenAIEmbeddingFunction } = chromadb; //Chroma provides a convenient wrapper around OpenAI's embedding API. This embedding function runs remotely on OpenAI's servers, and requires an API key. You can get an API key by signing up for an account at OpenAI.
const embedder = new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction({ openai_api_key: "your API Key" })
const client = new ChromaClient({ path: "path to your chroma Cient " }); //for example your client stored somewhere on Amazon, your path will be like: 'https://www.amazon.com/:8000'
After connecting the client, you will have access to the following methods:
Create Collection
const { ChromaClient } = chromadb;
const { OpenAIEmbeddingFunction } = chromadb;
const embedder = new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction({ openai_api_key: "your API Key" })
const client = new ChromaClient({ path: "path to your chroma Cient " });
const collection = await client.createCollection({ name: 'Your collection name', embeddingFunction: embedder })
return msg;
After creating a collection, you need to call the getCollection method each time to work with it.
Get Collection
const { ChromaClient } = chromadb;
const { OpenAIEmbeddingFunction } = chromadb;
const embedder = new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction({ openai_api_key: "your API Key" })
const client = new ChromaClient({ path: "path to your chroma Cient " });
const collection = await client.getCollection({ name: 'Your collection name' })
Before writing data, you need to send it for embedding creation.
Data which you get after embedding write to the variable msg.emb
Insert data to collection (collection.add)
const { ChromaClient } = chromadb;
const { OpenAIEmbeddingFunction } = chromadb;
const embedder = new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction({ openai_api_key: "your API Key" })
const client = new ChromaClient({ path: "path to your chroma Cient " });
const collection = await client.getCollection({ name: 'Your collection name' })
const create =await collection.add({
ids: [`your vectors id`],
embeddings:msg.emb,
metadatas: ['your custom metadata'],
documents:'your document name'
})
Before getting data from collection, you need to send user request for embedding creation.
Data which you get after embedding write to the variable msg.emb
Get data from collection (collection.query)
const { ChromaClient } = chromadb;
const { OpenAIEmbeddingFunction } = chromadb;
const embedder = new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction({ openai_api_key: "your API Key" })
const client = new ChromaClient({ path: "path to your chroma Cient " });
const collection = await client.getCollection({ name: 'Your collection name' })
const result = await collection.query({
queryEmbeddings:msg.emb,
query_text: 'user request',
nResults: 2 // count of items which get on result
})
Usage Example:
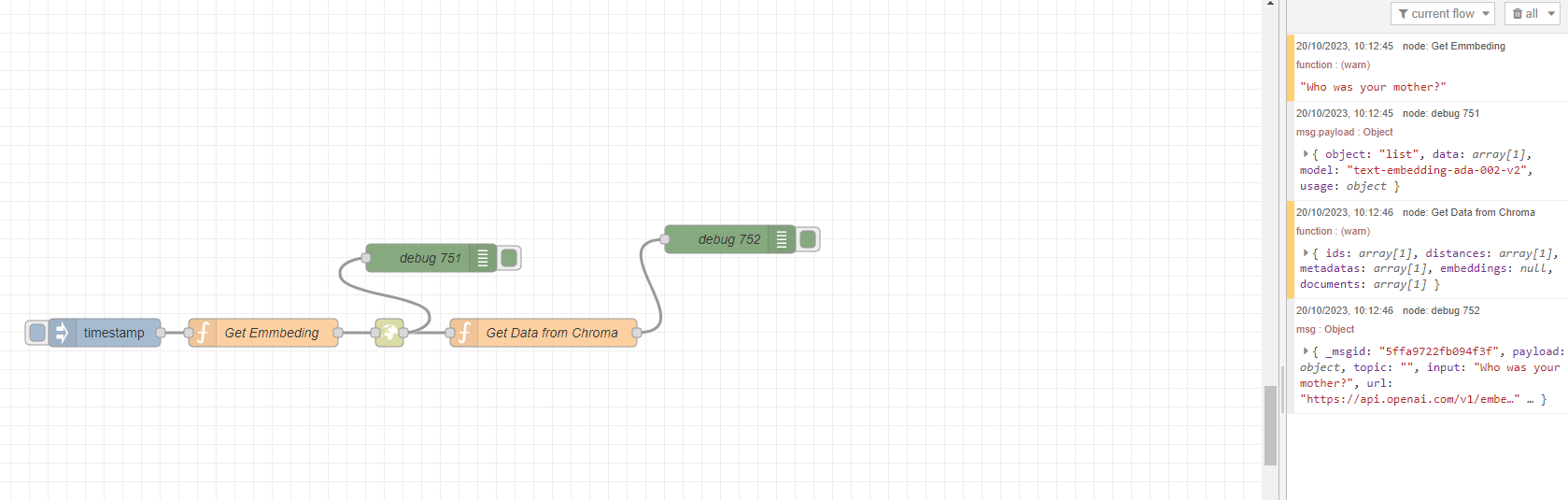
In this flow, we passed the user's question "Who was your mother?" to create a vector (embedding) and after this embedding, a query was made in the shevchenko collection in ChromaDB, and the resulting result was output to the msg.result variable
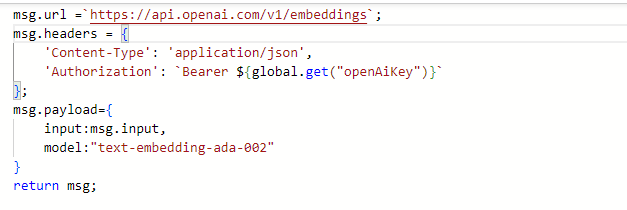
Example for creating embedding.
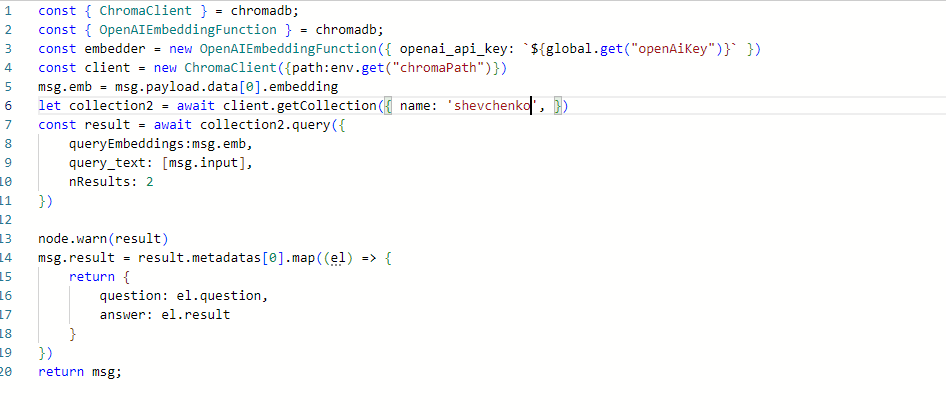
Performing a query in the shevchenko collection and processing the result.


Top comments (0)